EXAMINATIONS
The following examinations are performed at our practice:
Heart examinations
Performance diagnostics
Sleep apnea screening
Respiratory examinations
24-HOUR BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING
Blood pressure monitoring is used to diagnose high blood pressure (arterial hypertension).
Blood pressure readings do not always remain constant. Blood pressure naturally fluctuates throughout the day and can also be influenced by physical and emotional stress.
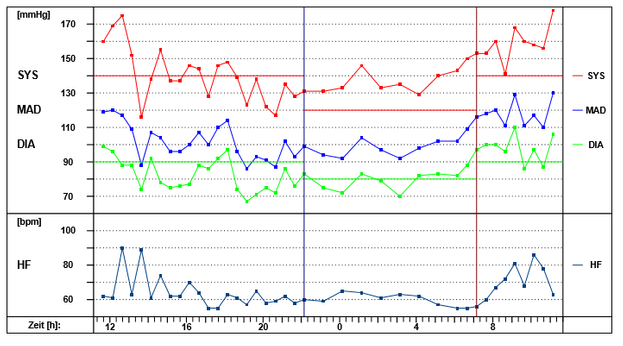
24-hour blood pressure monitoring is considered the gold standard for assessing the patient's blood pressure situation while they go about their day-to-day business. An automatic blood pressure monitor fitted to the upper arm takes the patient's blood pressure at pre-programmed intervals over the course of 24 hours; additional readings can be triggered by the patient themselves. By storing the data in a recorder, daily activities or perceived symptoms can be matched, which the patient documents in a log.
24-hour blood pressure monitoring provides the following information:
- Due to nervous tension, blood pressure readings taken at medical practices are often inaccurate (too high). 24-hour blood pressure monitoring makes it possible to distinguish between white coat hypertension and hypertension that requires treatment.
- Detection of nocturnal and stress-induced blood pressure regulation disorders that would otherwise go undetected.
- Assessment of therapeutic success of blood pressure medication.
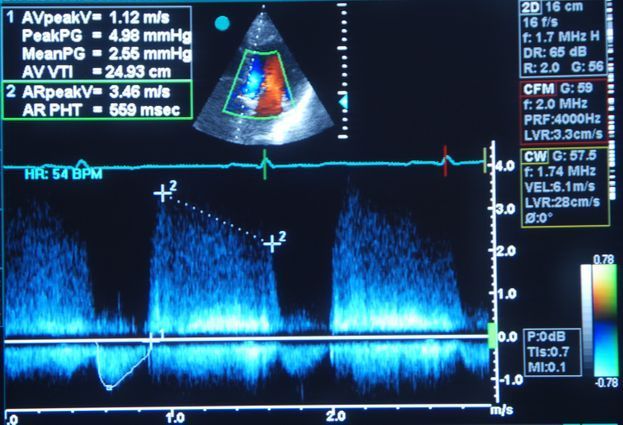
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
Alongside ECG, cardiac ultrasound is the most important non-invasive diagnostic procedure used in cardiology. The test can be used to image heart structures in temporal and spatial resolutions. This allows conclusions to be drawn about the size, function and wall thickness of the individual heart chambers, as well as the condition of the pericardium and the heart valves.
Echocardiography is used to assess the following:
- Pumping capacity of the heart muscle or quantification of a heart muscle weakness (heart failure)
- Wall movement disorders of the heart muscle as an indication of potential circulatory disorders of the coronary arteries (coronary heart disease)
- Follow-up checks in the case of heart attacks or heart surgery such as balloon dilatation (PTCA), stent implantation or bypass surgery
- Heart valve defects and follow-up checks after heart valve surgery
- Increases in pressure in the right side of the heart/pulmonary circulation (e.g. pulmonary embolism, chronic respiratory disease) or in the left ventricle (hypertensive heart disease)
- Risk of blood clots in the heart after a stroke
- Inflammation of the heart muscle (pericarditis/myocarditis)
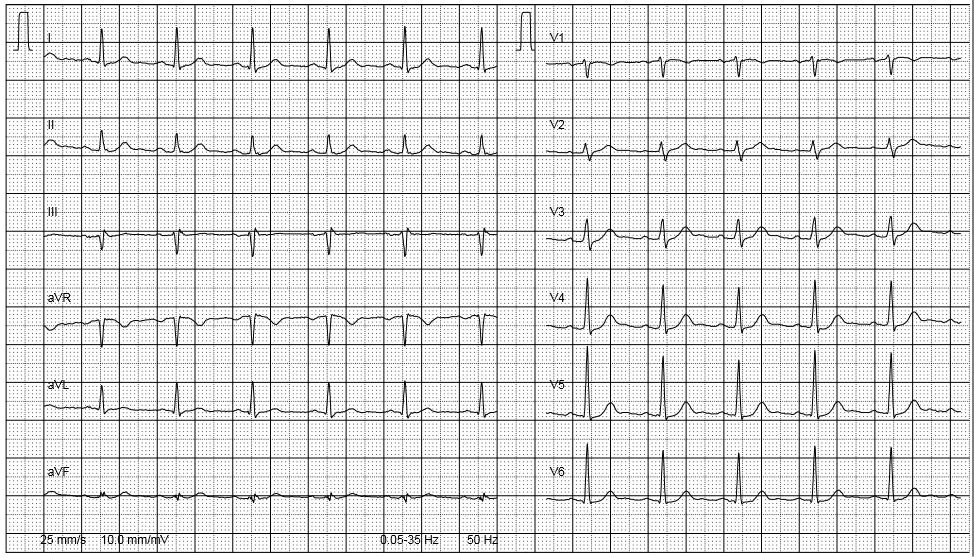
ELECTROCARDIOGRAM (ECG)
An ECG is the classic method of cardiac diagnostics. Each heartbeat or contraction of the heart muscle is preceded by an electrical impulse, which normally occurs in the sinus node (right atrium) and spreads via a conduction system of specialised cardiac muscle cells. In order to record the electrical activity of the heart muscle, electrodes are attached to the chest and extremities. The test is safe and painless for the patient.
An ECG can reveal the following:
- Circulatory disorders of the heart or a previous heart attack
- Heart arrhythmia
- Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis) or pericardium (pericarditis)
- Thickening of the heart wall (hypertrophy)
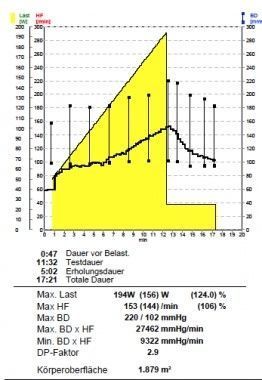
ERGOMETRY/ECG STRESS TEST
Ergometry is used to test the heart under controlled physical exertion with simultaneous, continuous ECG monitoring and blood pressure monitoring. The level of exertion is increased gradually or continuously by means of computers. The stress phase usually lasts 8 to 12 minutes. The test is completed when the target functional capacity calculated for the individual has been reached, or earlier in the event of physical exhaustion, chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, serious ECG changes, or abnormalities in blood pressure.
A stress ECG can reveal the following:
- Circulatory disorders of the heart
- Stress induced heart arrhythmia
- Incorrect blood pressure under stress
- Individual functional capacity
Ergometry as a performance test
Performance diagnostics is not only relevant for ambitious athletes. A precise performance analysis is especially useful for patients with pre-existing conditions (e.g. diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease) for whom a supervised exercise programme forms an important part of their treatment.
Ergometry can be used to evaluate the individual's current level of physical performance and to derive recommendations for creating a sensible, goal-oriented training programme.
CONTINUOUS ECG
This test is used primarily for the diagnosis of heart arrhythmia.
Reasons for performing a continuous ECG include:
- Unexplained dizziness
- Syncope (short-term loss of consciousness)
- Clarifying the causes of a stroke
- Dangerous arrhythmia in the case of myocardial insufficiency or infarction
A continuous ECG is used as the method of investigation as arrhythmia often only occurs for a few minutes each day, during rest periods or at night. As with a normal ECG, three or more electrodes are attached to the chest. Using a small, portable recording device, the heart rate can be monitored continuously over a period of 24 hours for up to seven days while the patient goes about their usual business and makes a note of any symptoms.
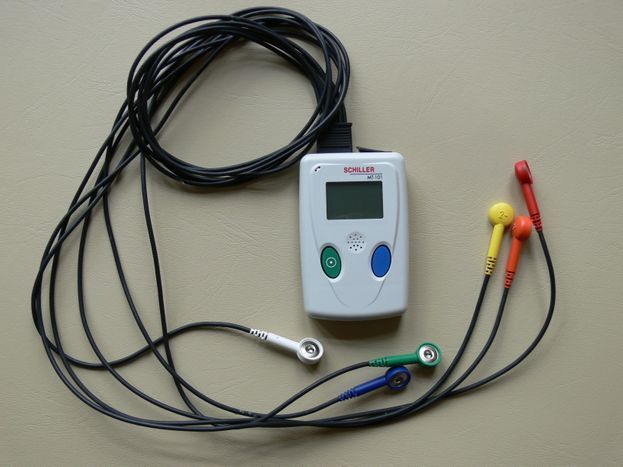

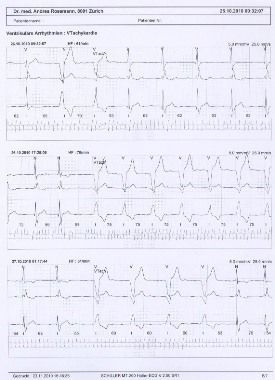
If the continuous ECG fails to diagnose a rhythm disorder that could put the patient at risk, a further option is an IMPLANTABLE HEART MONITOR/EVENT RECORDER.
IMPLANTABLE HEART MONITOR/EVENT RECORDER
Heart arrhythmia often occurs at longer intervals and can therefore not be detected with a conventional ECG. If dangerous heart arrhythmia cannot be diagnosed with a continuous ECG either, another option is to try an implantable heart monitor.
An event recorder may be implanted for the following reasons:
- If the cause of a stroke is unknown, it is essential to check whether the patient is suffering from atrial fibrillation, so that the chances of a further stroke can be reduced
- Unexplained syncope (brief loss of consciousness) with suspicion of an underlying rhythmogenic cause
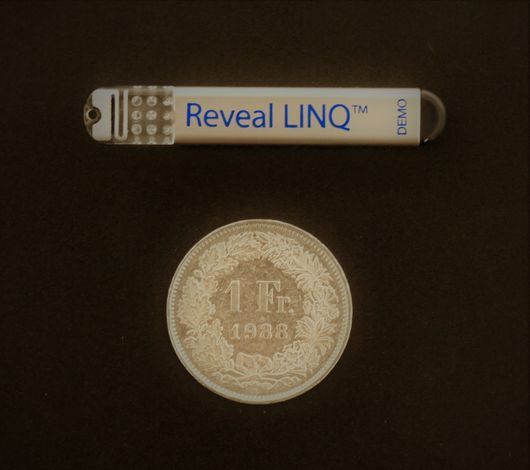
The implantable heart monitor is a kind of miniature 'mobile' ECG device that is inserted under the skin in a minimally invasive procedure and can monitor the heart rhythm for up to three years. At our practice, we use the Reveal LINQ from Medtronic. With a volume of 1.2 cc and weighing just 2.5 g, it is the smallest heart monitor available on the market.
In the event of abnormalities, the heart monitor automatically stores an ECG, which the doctor can consult on an external device during the patient's next consultation. In addition, the Reveal LINQ automatically sends the recorded ECG data to the MyCareLink patient monitor each night, which transmits the data via the mobile network to a secure website, where the doctor can check it and contact the patient if their heart rhythm is irregular.
The heart monitor is MRI compatible, meaning that any necessary MRI tests can be performed. The Reveal LINQ is inserted under the skin in the chest area and is not visible in most patients.
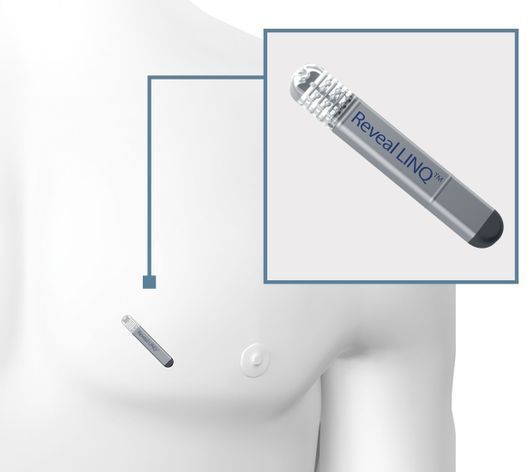
Copyright © Medtronic 2018
PACEMAKER CHECKS
Pacemakers are used to treat heart arrhythmia, especially when a slow heartbeat or pauses lead to dizziness and unconsciousness (syncope). The device stimulates the heart muscle with electrical impulses in order to make it contract.
Pacemaker aftercare:
After being implanted, the devices must be regularly checked (every 6 to 12 months) to make sure they are working properly. This is done telemetrically via a manufacturer-specific programming head that is placed on the skin directly above the pacemaker casing. The battery status and, thus, the remaining operating time of the pacemaker unit is also checked. This determines the frequency of the follow-up checks.
We currently perform follow-up checks for pacemakers by the manufacturers St. Jude Medical, Medtronic and Biotronic at our practice. Other pacemakers are checked in collaboration with the relevant rhythmology departments of the hospitals.
Note: Please bring your pacemaker identification card with you to your appointment - thank you!
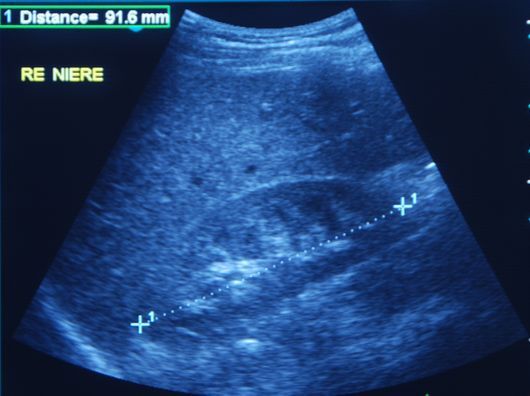
ABDOMINAL ULTRASOUND
With an abdominal ultrasound, numerous diseases of the abdominal organs can be diagnosed at an early stage and an appropriate course of treatment can be initiated. Examples include:
- Gallbladder: stones, inflammation
- Liver: fatty liver, cirrhosis incl. elastography ((determination of the stiffness of the liver tissue)
- Kidneys: kidney zysts, kidney stones, atrophic kidneys, changes due to diabetes, high blood pressure
- Dilatation or calcification with circulatory disorders of the abdominal artery and veins
- Diseases of the spleen, pancreas, etc.
- Determination of residual urine volume
- Prostate: Enlargement, Calcifications etc.
- Uterus: Uterine Myoma
Tumours can also often be detected at a very early stage using this method.
An ultrasound scan is not harmful, i.e. no X-rays are used, no contrast medium that is harmful to the kidneys is needed, and the examination is completely painless. To ensure optimum results, the patient should not consume any food or liquids for approximately eight hours before the scan.
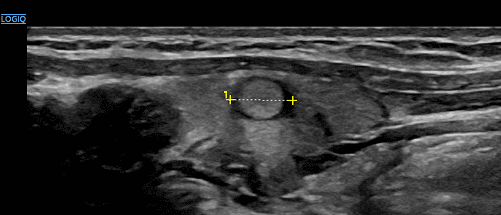
THYROID ULTRASOUND
An ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland can be used to assess the size, condition and blood circulation of the organ in the event of functional problems, and can also be used to detect abnormalities and rule out malignant diseases.
No special preparations are needed on the patient's part.
BREAST ULTRASOUND (MAMMA)
The ultrasound examination of the female breast (breast ultrasound) is a complementary procedure to mammography (X-ray examination of the breast).
Advantages of breast ultrasound are:
- Painless examination and free from radiation exposure (X-ray)
- Particularly suitable for small breasts and dense glandular tissue
- Cancer detection rate can be increased
- Palpatory findings can be assessed better, e.g. differentiation between cysts and solid findings
- It is very suitable in women younger than 30 years of age with pain of the breasts (mastodynia)
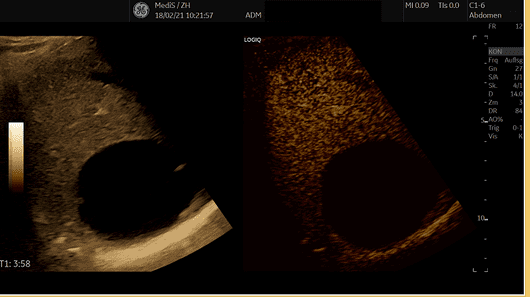
CONTRAST-ENHANCED ULTRASOUND (CEUS)
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound examination (CEUS) is a new technique which uses gas-filled microbubbles as a contrast medium. Therefor the visibility (echogenicity) of the blood is increased. There is no radiation exposure or impairment of the kidney function (nephrotoxicity). CEUS thus allows the blood flow and tissue perfusion of various organs and structures to be displayed in real time. The combination of the ultrasound contrast agent with the most modern ultrasound devices is a flexible and inexpensive examination method, which is in many cases equivalent or even superior to the existing examination methods such as CT, MRT and nuclear medicine technology.
We offer the following fields of application for CEUS:
- Investigation of liver changes such as hemangiomas, focal nodular hyperplasia, cystic changes, liver carcinoma or metastases.
- Investigation of kidney changes such as complicated kidney cysts (according to the Bosniak classification), angiomyolipoma, benign and malignant kidney tumors.
- Investigation of changes in the pancreas such as benign and malignant pancreatic tumors
- Investigation of changes of the breast
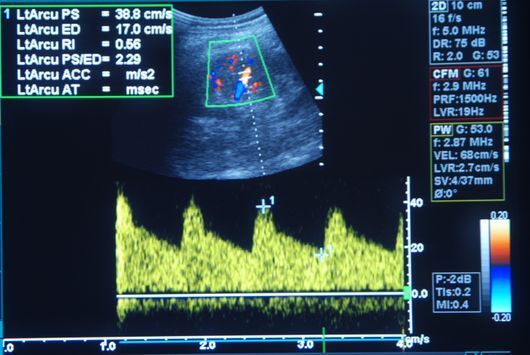
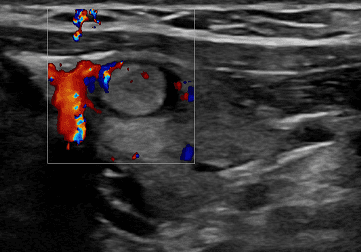
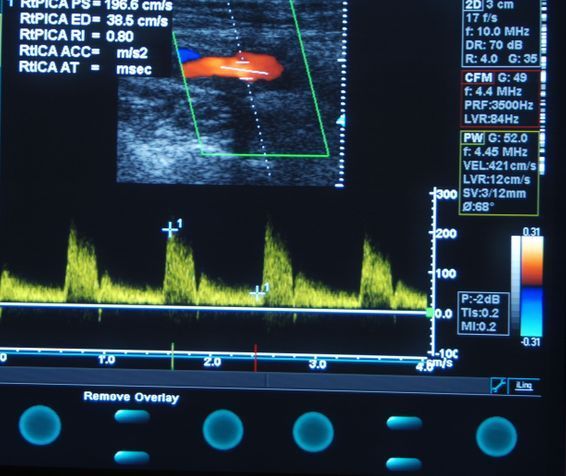
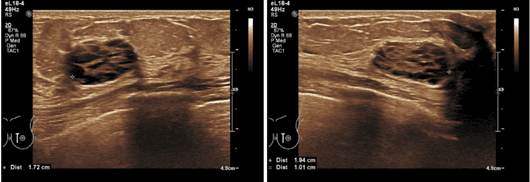
VASCULAR ULTRASOUND (DOPPLER AND DUPLEX)
Ultrasound is an elementary diagnostic tool used in Angiology and Phlebology. In contrast to angiographic vessel images in X-rays with catheter procedures, this investigation is a non-invasive way of imaging the blood vessels. The advantages are that no X-rays are used, no contrast medium that is harmful to the kidneys is needed, and the examination is completely painless.
Among other things, the examination assesses the following:
- Calcifications, stenosis, vascular occlusions and circulatory disorders of the arteries
- Vasodilatation (aneurysms)
- Leg vein thrombosis
- Varicose veins
FUNCTIONAL VASCULAR DIAGNOSTICS
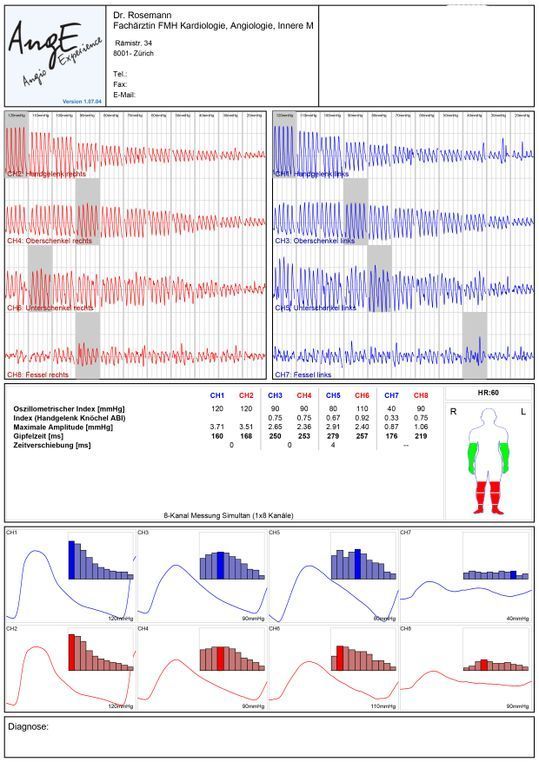
ARTERIES – OSCILLOGRAPHY
Similar to the method of blood pressure monitoring, cuffs on both wrist and ankle joints are used to simultaneously record the volume fluctuation occurring in these extremities during the cardiac cycle. The ankle-brachial index (ABI) detected serves as a screening test for the presence of a peripheral arterial occlusive disease (intermittent claudication) and can also be used to predict cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes.
If the ankle-brachial index is abnormal and circulatory disorders of the leg arteries are suspected, a segment oscillography is performed. Here the cuffs are placed on both sides of the wrist, upper and lower leg and forefoot. This more detailed analysis allows for layer localisation of vascular constrictions or occlusions. An ultrasound scan can then be used to look for the narrowing of the blood vessel in the identified region, before deciding on the appropriate treatment.
PULSE WAVE VELOCITY (PWV) for EARLY DETECTION OF ARTERIOSCLEROSIS
The pulse wave velocity (PWV) is the speed at which the pressure wave passes through the arteries of an organism. Premature vascular ageing is one of the main symptoms of arteriosclerosis. Substances build up in the walls of the arteries, leading to arterial stiffness, which can be detected by an increased PWV.
The examination is painless. As with oscillography, cuffs are applied to both wrists and ankles, as well as an ECG clamp to each wrist. Based on the changes to the vascular system associated with the pathological values, the PWV measurement can provide information about mortality in the case of diabetes mellitus or terminal renal insufficiency, for example, and also help to assess general cardiovascular risk factors.
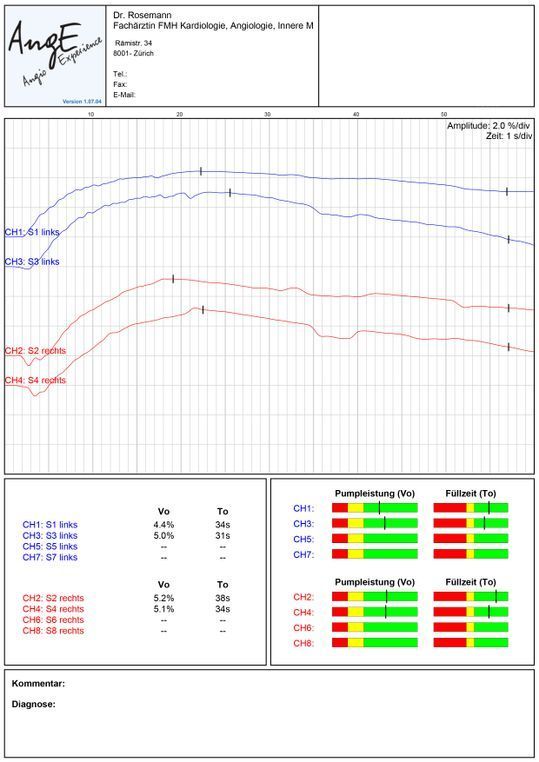
VEINS – DIGITAL PHOTOPLETHYSMOGRAPHY / LIGHT REFLECTION RHEOGRAPHY (DPPG/LRR)
This examination, also known as a muscle pump test, measures the functionality of the veins and venous valves. When the calf muscles are tensed, the blood flow into the superficial veins decreases; when the muscles are relaxed, it increases again. This leads to a slight change in skin contrast, which the sensor detects. If the veins are refilled at a lower speed when relaxing the muscles, this indicates weak veins in the case of varicose veins.
SLEEP APNEA SCREENING
Sleep apnea syndrome (SAS) is a sleep-related respiratory disorder associated with a periodic reduction in the frequency of breathing (hypopnea) or respiratory arrest (apnea) during sleep, causing less oxygen to be supplied to the brain.
Symptoms that may indicate SAS include:
- Snoring
- Feeling very tired during the day, to the point of falling asleep (microsleep)
- Headaches on awakening (feeling shattered)
- Dizziness, especially after waking up
- Dry mouth on awakening
- Difficulties concentrating, poor memory
- Restless sleep, sleep disturbances
However, there are many reasons for not being able to sleep well from time to time. Even snoring is by no means a definite sign of having a respiratory disorder. Almost half of all people in Switzerland occasionally make snoring noises while sleeping, but only about 10% of them actually suffer from sleep apnea (some 400,000 people).
Outpatient sleep apnea diagnosis
The first step in determining whether someone is suffering from sleep apnea is to use a small screening device. We use the ApneaLinkTM Air at our practice. The patient can wear it comfortably overnight at home. It uses two sensors during sleep to record respiratory flow and snoring via a nasal cannula, as well as oxygen saturation and pulse rate via an oximeter.
Copyright © ResMed 2018
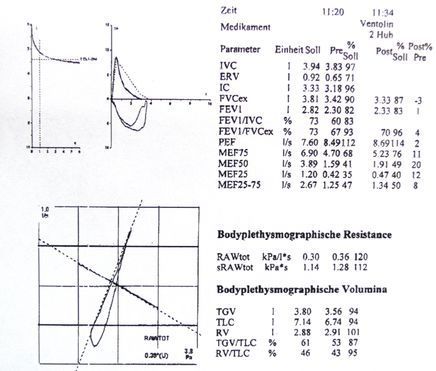
LUNG FUNCTION TEST (SPIROMETRY)
Constrictions of the airways and changes in lung capacity can be detected by measuring airway resistance and breathing volumes at maximum inhalation and exhalation. Medication may also be administered as a spray, if necessary, such as in a provocation (methacholine) test, to determine whether the bronchial system is overreactive/hyperreactive or to assess the effectiveness of drug therapy (bronchospasmolysis).
The information provided by spirometry can be used to:
- Determine whether shortness of breath is caused by heart disease or lung disease.
- Assess whether long-term nicotine use has already caused lung damage
- Diagnose and monitor the progress of respiratory diseases (e.g. bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pneumopathy/COPD, pulmonary over-inflation/emphysema)
Opening hours:
- Mon - Fri
- - -
- Sat - Sun
- Closed
Phone consultation:
- Mon - Fri
- - -
- Sat - Sun
- Closed
Appointments will be made according to agreement.